Inprocess 3D
Discover Inprocess 3D, an advanced three-dimensional equipment visualization environment for process engineering, designed to represent, analyze, and understand industrial unit operations in a virtual environment.
Index of Unit Operations

Aircooler
An aircooler is a heat exchanger equipment which consist of a tube bundle over which air is blown or drawn by fans mounted above or below the tubes. Aircoolers are used mainly when cooling water is not available or in short supply; when water supply results in significant increase in costs, and when there are concerns for water pollution.

Absorption in Packed Columns
Gas absorption is a separation process in which soluble components of a gas mixture are dissolved (absorbed) in a liquid. In this way, one or more constituents of the gas can be removed from the mixture. The solubility difference between the gas mixture and the compound to be absorbed in the liquid and the rate of mass transfer are the fundamental physical principles of this process.
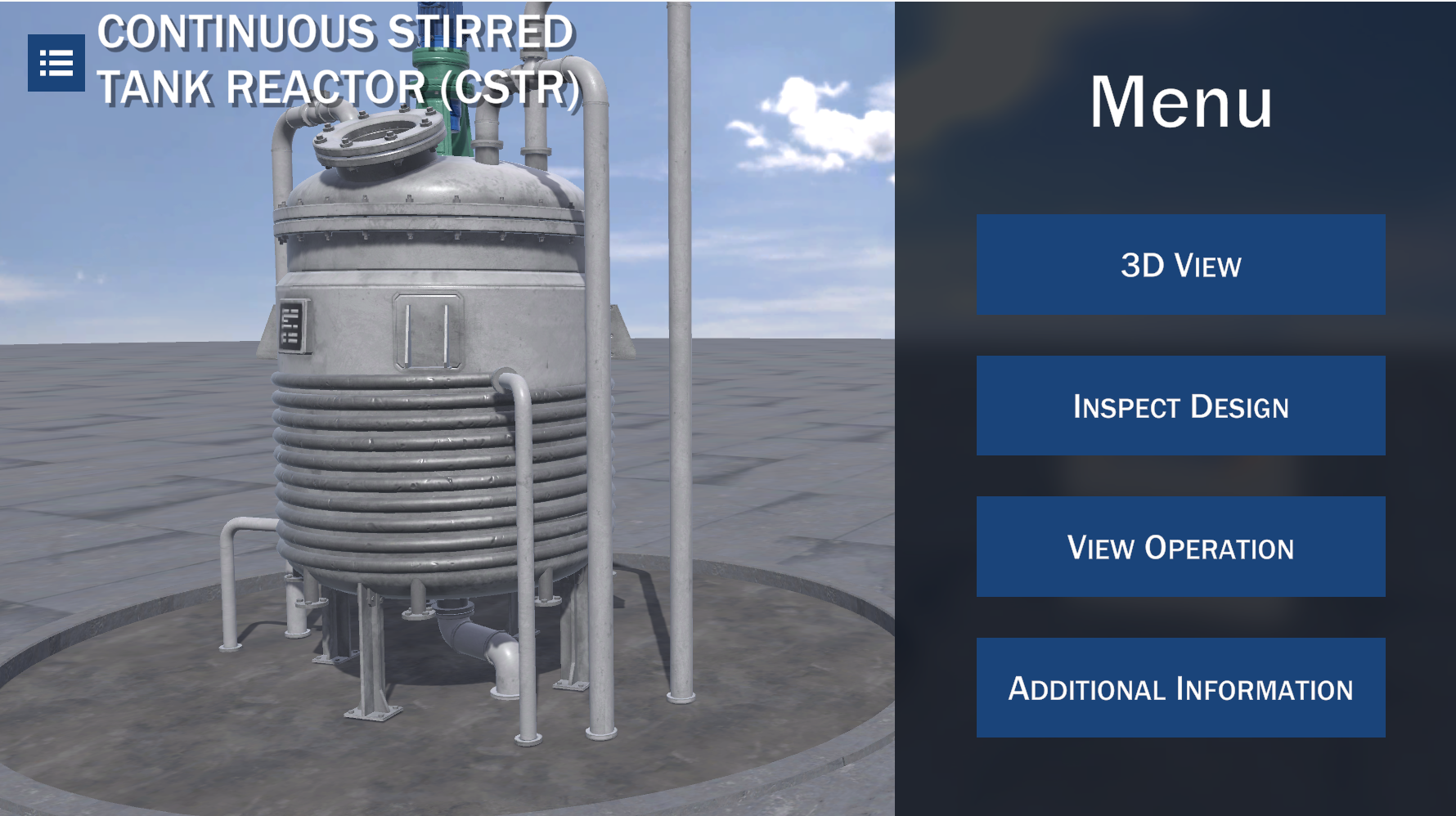
Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor (CSTR)
A continuous stirred tank reactor (CSTR), or backmix reactor, is a type of reactor normally equipped with an impeller or other mixing device, in which the reactants are fed to the reactor and the products withdrawn continuously and thus, it works at constant volume. In an ideal CSTR, the conditions are uniform throughout, and the conditions of the effluent are the same as the conditions in the tank.

Centrifugal Compressor
A centrifugal compressor, also called radial compressor, is a device used to move compressible fluids and to increase their pressure by the conversion of kinetic energy. In a centrifugal compressor, the compressible fluid enters axially in the impeller and it discharges radially.
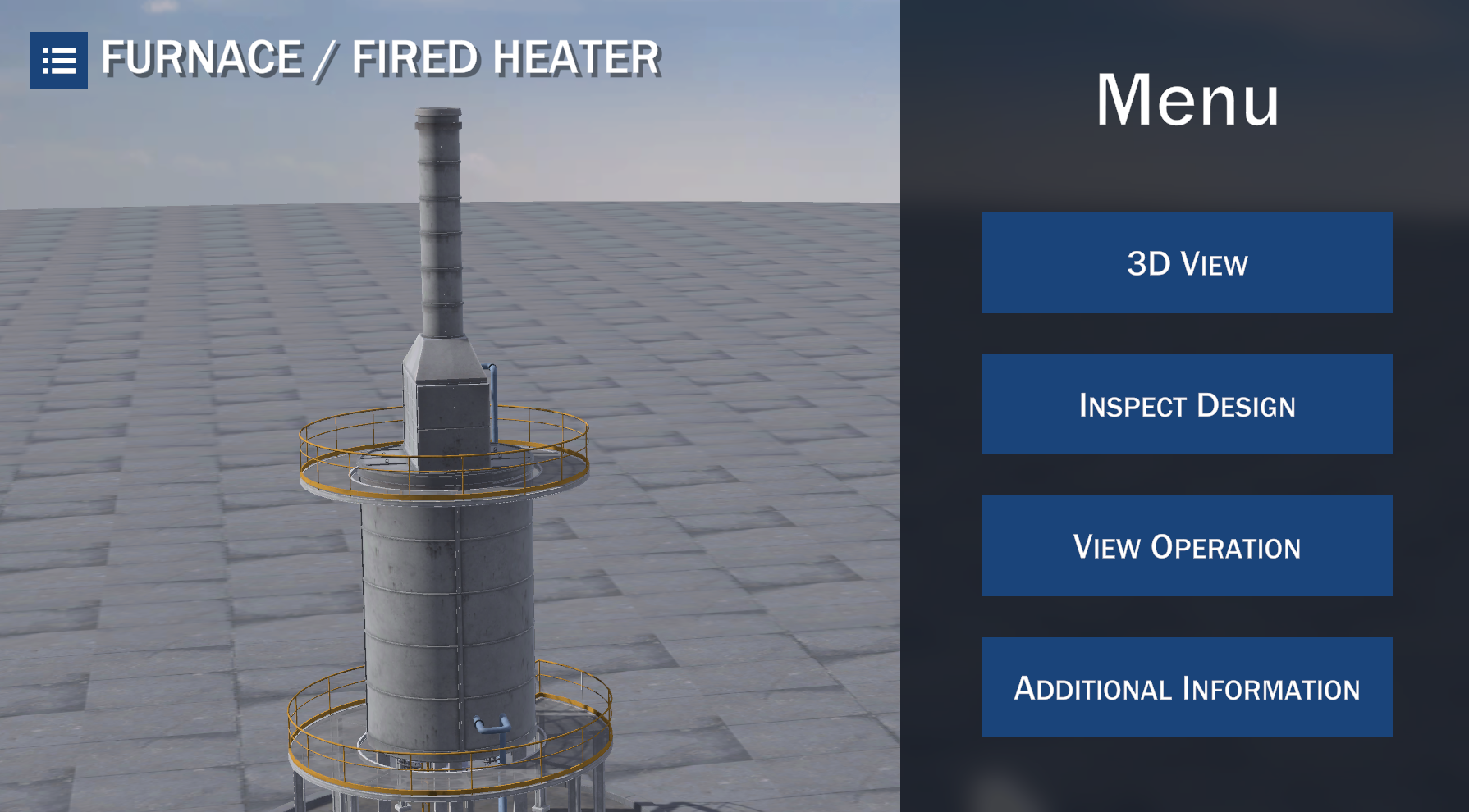
Furnace / Fired Heater
A furnace, also called fired heater, is a heat transfer equipment which uses hot combustion gases (flue gas) to rise the temperature of fluids flowing through different arrangements of tubular coils. Furnaces are used not only to provide heat to process streams, but even as a reactor which provides the required heat for a reaction to take place.

Distillation in Trayed Columns
A trayed distillation column is a device used for the separation of a mixture into its components, based on the volatility difference between them. In such a device, distillation is carried out by using individual units coupling or interconnected to each other creating different separated zones along the column with different temperature, pressure, composition, and/or phase state each one.
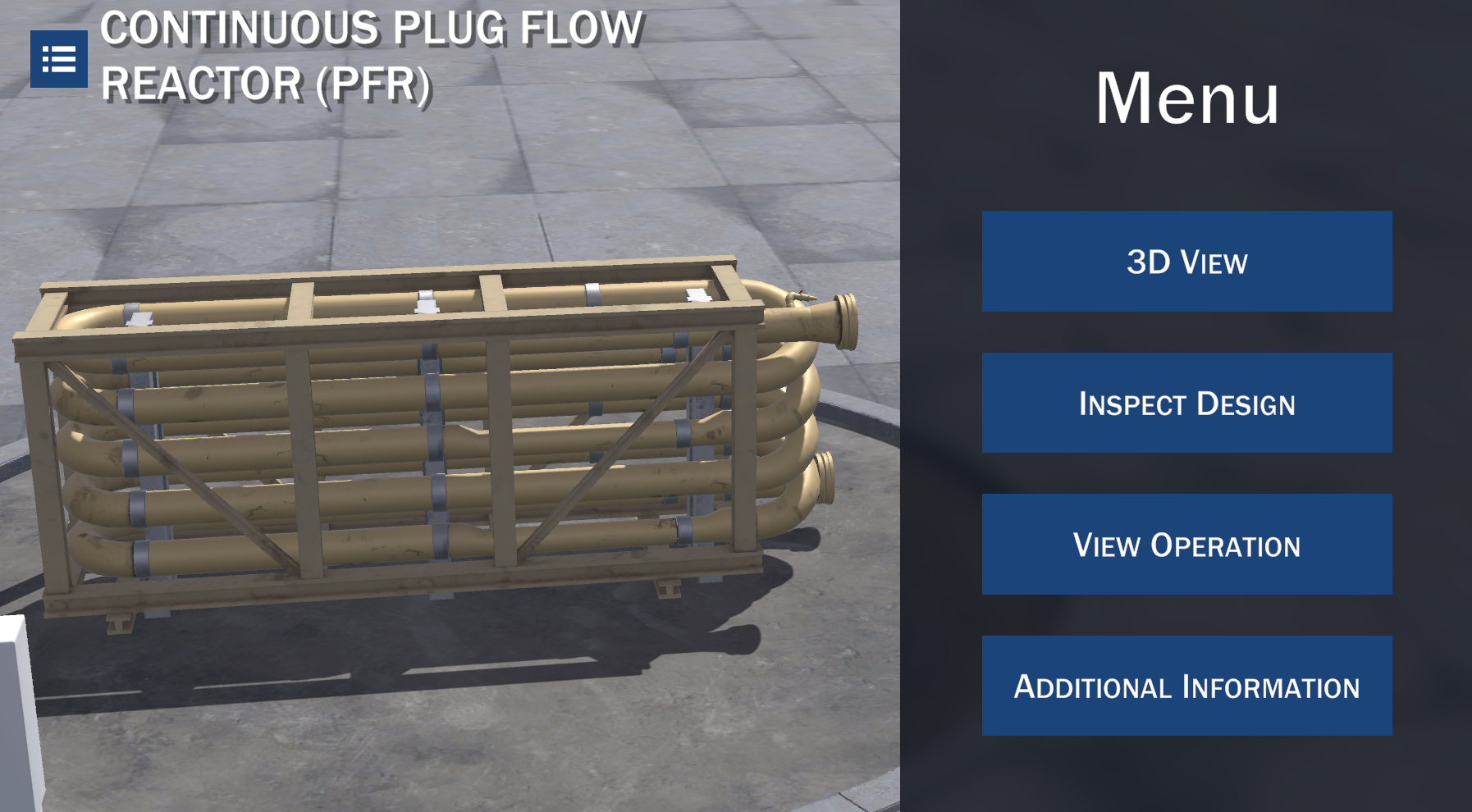
Plug Flow Reactor (PFR)
A reactor is an equipment in which chemical reactions take place in certain operating conditions, so raw materials are converted into products. A Continuous Plug Flow Reactor, also known as tubular reactor, consists of a cylindrical tube in which the reactants are continuously fed, reacted and therefore, consumed as they flow through the reactor. The conditions in the reactor (concentration and temperature) are not uniform.
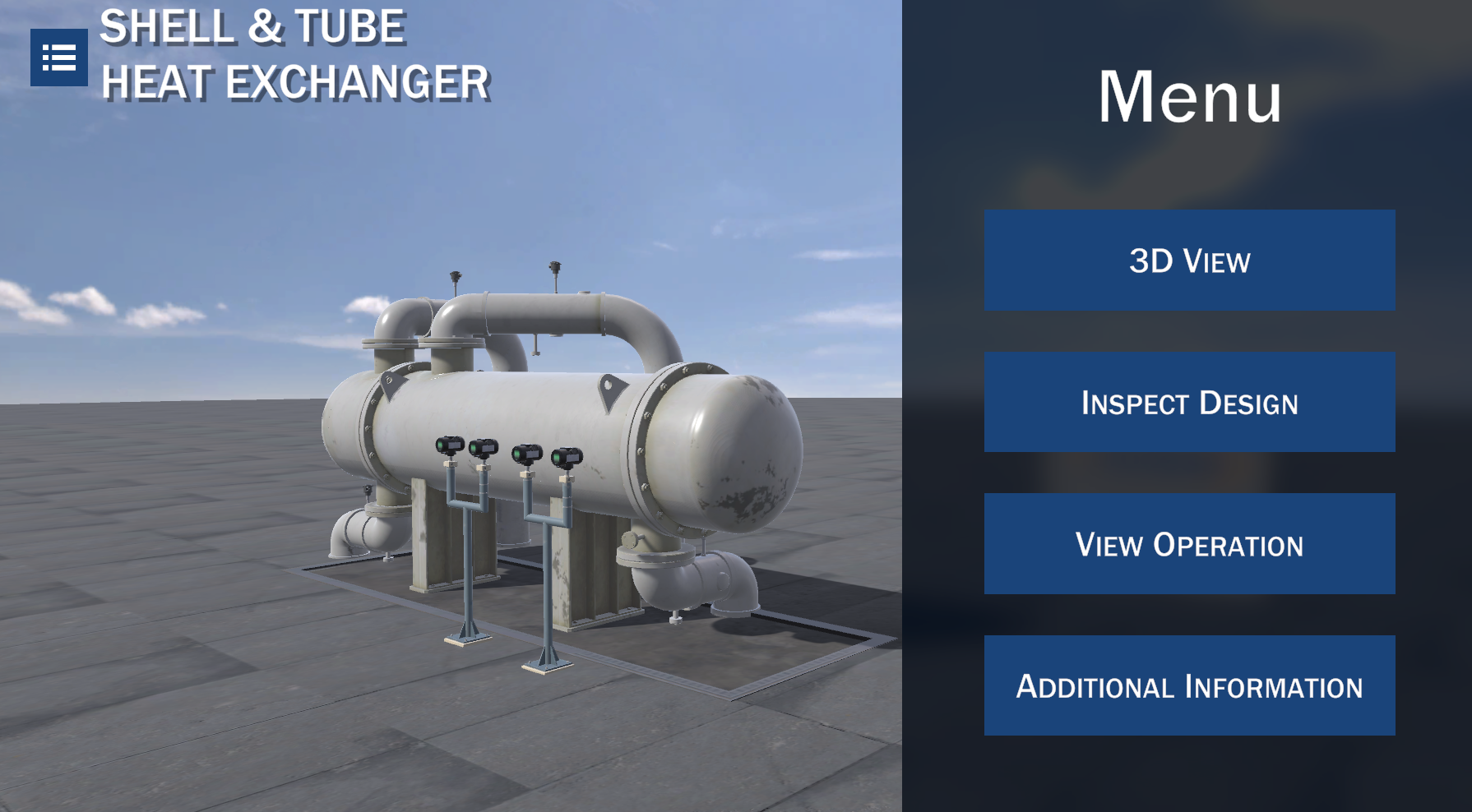
Shell and Tube Heat Exchanger
The shell and tube heat exchanger is a type of design for exchangers which consists of a bundle of tubes inside a cylindrical shell, where the two fluids do not mix with each other. These heat exchangers can be designed for a wide range of pressure and temperatures.
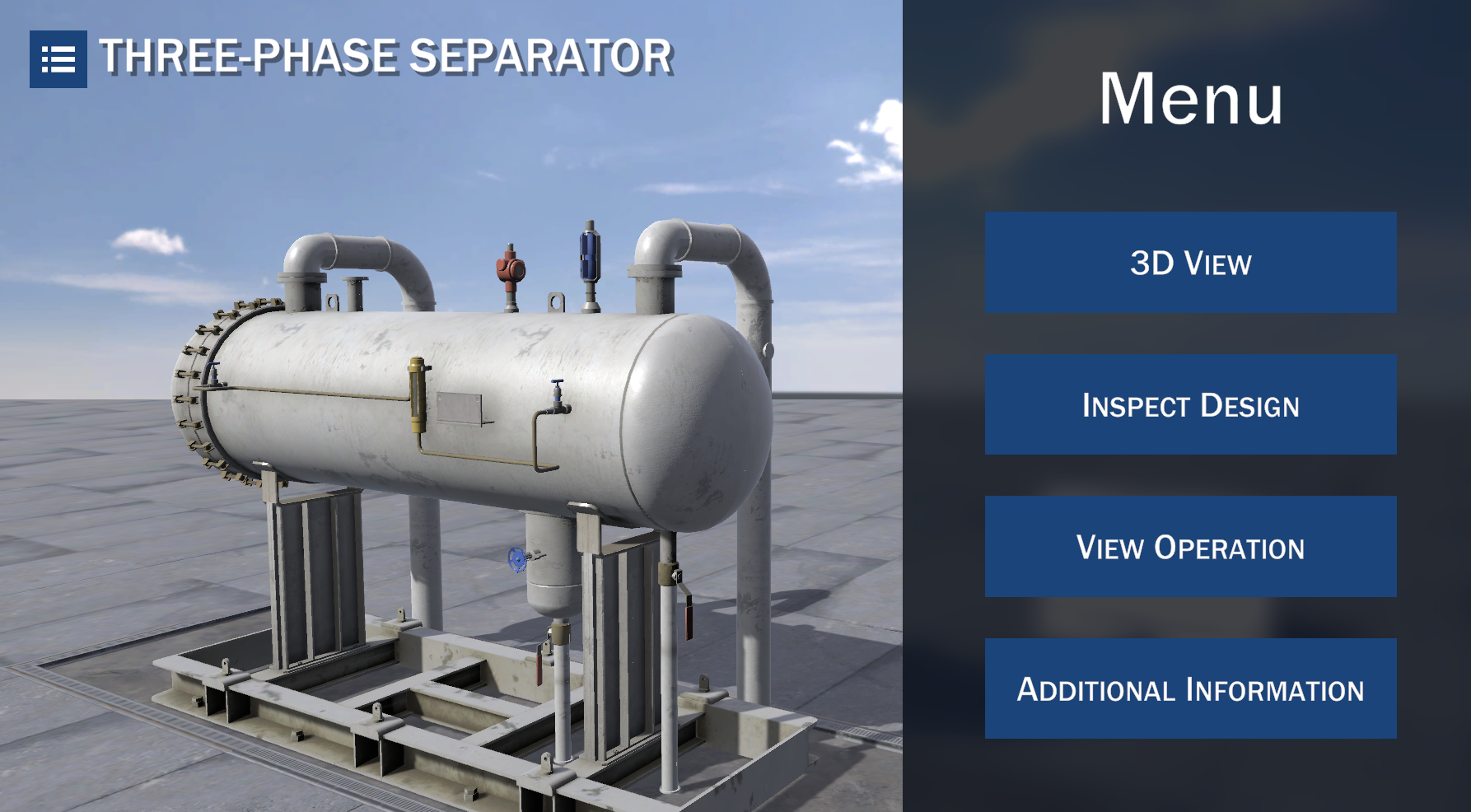
Three-Phase Separator
A three-phase separator is a vessel used for the separation of three phases: gas, light liquid phase, and heavy liquid phase. The working principles of the three-phase separator are: momentum variation, gravity force, and coalescing. For this reason, the fluid phases must be immiscible and have different densities (Password: Free_3Phase)
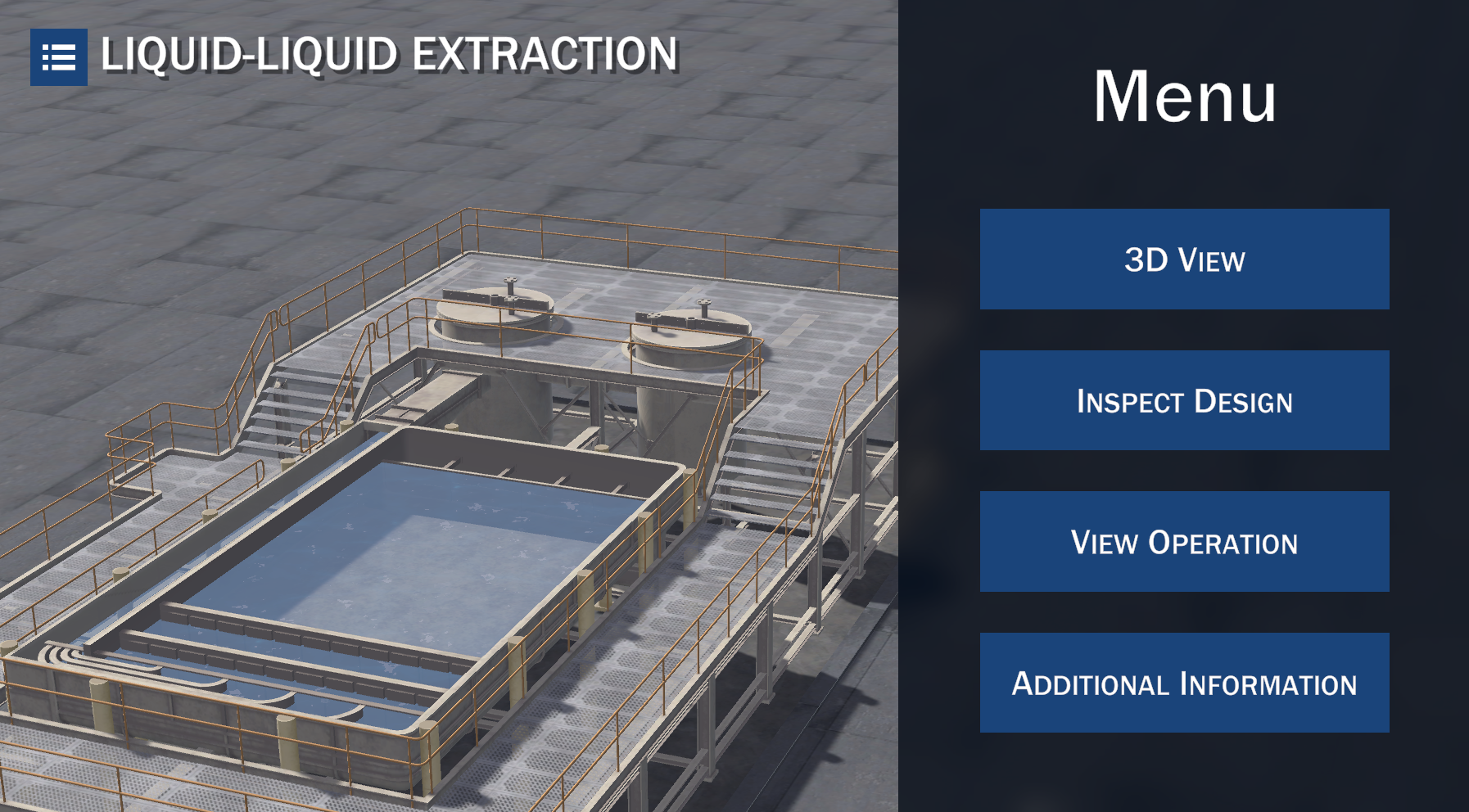
Liquid-Liquid Extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction is a separation process of one or more components present in a liquid by putting them in contact with a second immiscible liquid (solvent). This process implies the mass transfer of a solute between the two liquids and can be of different complexity. This training material is based on the simplest example: extraction of one component from a binary mixture into a second immiscible liquid.

Process Control and Instrumentation
During the plant operation it becomes necessary to monitor and control the key process variables. This is achieved by the use of instruments and controls. Instruments are often incorporated in automatic control loops which in turn act over a final control element. This material is based on one final control element type: control valve. The main parts and the operation of this device are detailed herein.



